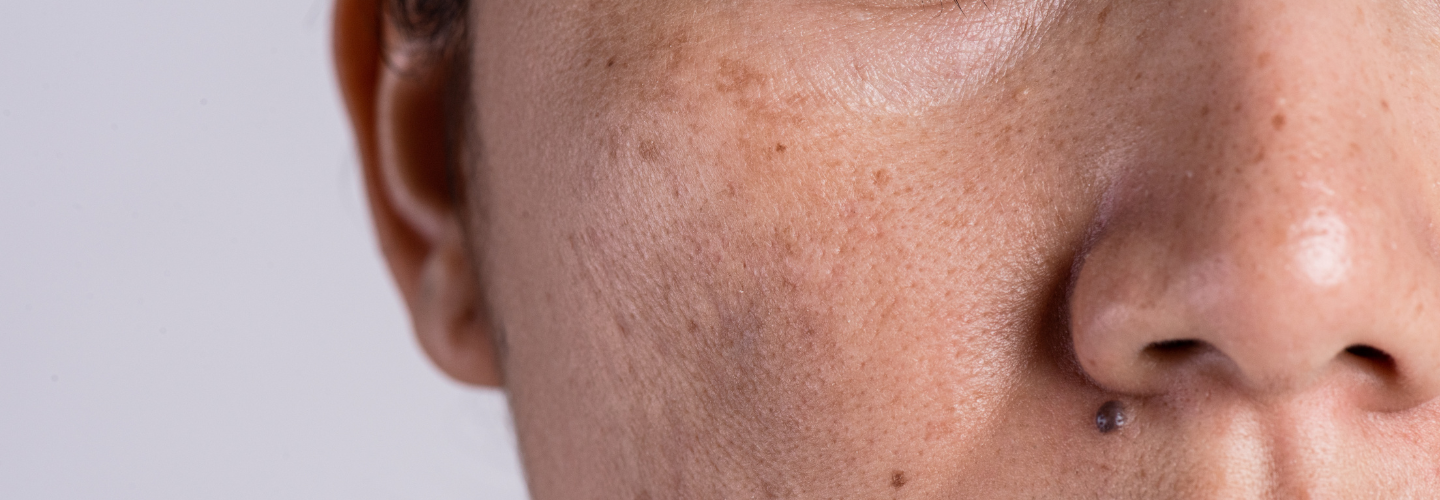
Melasma, often recognized as brown spots on the skin, can be a source of concern for many individuals. These pesky spots, characterized by dark pigmentation on the skin, can be triggered by various factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, and genetics. With advancements in skincare and dermatology, 2024 brings forth a diverse range of topical and oral treatments designed to address melasma effectively. The skincare industry has witnessed remarkable advancements in treating brown spots, with Pynocare emerging as a promising solution.
Understanding Brown Spots on Skin
Melasma is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects women, especially those with darker skin tones. It is characterized by the development of brown or grayish-brown patches on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and chin. The exact cause of melasma is not fully understood, but it is believed to be influenced by hormonal changes, sun exposure, genetics, and certain medications.
The Role of Melanin
Melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes, plays a central role in melasma. The skin contains specialized cells called melanocytes, which produce melanin in response to various stimuli, including exposure to sunlight.
1. Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays is a significant trigger for the occurrence of brown spots in melasma. When the skin is exposed to UV rays, melanocytes produce more melanin as a defense mechanism against potential DNA damage caused by sunlight. This increased melanin production often leads to the formation of brown spots, especially on areas of the skin that receive the most sun exposure, such as the face.
2. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly an increase in estrogen and progesterone, can contribute to the development of melasma and the occurrence of brown spots. This is why melasma is often associated with conditions such as pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, and hormonal therapy. Hormonal changes may stimulate melanocytes or alter the way melanin is distributed in the skin, leading to the formation of brown spots.
3. Genetic Predisposition: Genetics also play a role in the occurrence of brown spots in melasma. Individuals with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Specific genetic factors may influence how the skin responds to sun exposure and hormonal changes, contributing to the formation of brown spots.
4. Inflammation and Other Triggers: Inflammation and certain medications may act as triggers for the occurrence of brown spots in melasma. Chronic inflammation can disrupt the normal functioning of melanocytes, leading to increased melanin production and the manifestation of brown spots. Additionally, some medications may contribute to melasma as a side effect.
The development of brown spots in melasma is a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Understanding its occurrences is crucial for effectively managing and addressing this common skin condition. Considering these factors is essential for devising effective treatment strategies and preventive measures.
Effective Treatments for Brown Spots
The good news is that there are effective treatments available to help fade and even eliminate those brown spots for good. In recent years, both topical and oral treatments for brown spots on the skin have advanced significantly, providing individuals with a range of options to achieve more even-toned and healthier skin. Whether you prefer a topical cream or a supplement that works from within, there is a solution that can help you regain your confidence and achieve the complexion you desire.
Topical Treatments
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a commonly used topical treatment for melasma. It is used as a skin-lightening agent and works by inhibiting the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for the brown spots.
Hydroquinone reduces brown spots in melasma through a few key mechanisms by targeting melanin production, and transfer, and promoting skin renewal. However, caution is advised as long-term use may lead to side effects, such as skin irritation or a condition known as ochronosis. It is important to note that hydroquinone should be used under the guidance of a dermatologist, as long-term use or misuse can lead to side effects such as skin irritation and potential rebound hyperpigmentation.
Retinoids
Retinoids are derivatives of vitamin A and are renowned for their ability to promote skin renewal, improve texture, and address various skin concerns. In the context of melasma, retinoids, such as tretinoin, play a vital role in targeting hyperpigmentation and reducing the appearance of brown spots. Retinoid creams help in melasma by promoting skin cell turnover, inhibiting melanin synthesis, and stimulating collagen production.
However, retinoids can cause skin dryness and irritation, so it’s important to start with a low concentration and gradually increase as tolerated. Precautions also include potential irritation, especially for those with sensitive skin, and the need for sun protection due to increased sensitivity. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should avoid using retinoids due to potential risks to the developing fetus or infant. Consultation with a healthcare professional is important in such cases.
Vitamin C Serums
Vitamin C serums contribute to a brighter complexion and can be effective in reducing pigmentation. Topical vitamin C serums can help brighten the skin, reduce oxidative stress, and contribute to a more even skin tone. Vitamin C acts as a shield against oxidative stress, protecting the skin from external factors that can trigger melasma and supporting overall skin health. Vitamin C also inhibits the activity of tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin synthesis. This helps reduce the production of melanin, lightening brown spots and promoting a more even skin tone.
Regular use of vitamin C serum brightens the skin by reducing the appearance of existing brown spots and preventing the formation of new hyperpigmentation. However, individuals with sensitive skin should introduce these products gradually to avoid irritation. For optimal usage, while vitamin C provides some level of protection against UV damage, it should not replace sunscreen. Daily application of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF is essential to prevent further pigmentation and safeguard the skin.
Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring acid that is effective in treating melasma. Azelaic acid inhibits the activity of tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin synthesis. By regulating melanin production, it gradually reduces the intensity of brown spots associated with melasma. The regular use of azelaic acid promotes a more even skin tone by reducing hyperpigmentation and addressing the underlying causes of melasma.
Azelaic acid creams are available both over-the-counter and by prescription. It is generally well-tolerated, but some individuals may experience mild skin irritation. It is crucial to start with a lower concentration of azelaic acid and gradually increase usage to minimize the risk of irritation. It is also important to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF daily to prevent further pigmentation and protect the skin as it increases skin sensitivity to sunlight.
Oral Treatments
Oral Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid, when taken orally, has shown promise in inhibiting the pathways that lead to excess pigmentation. It is believed to help regulate melanin production and improve the appearance of brown spots. Tranexamic acid inhibits the activation of an enzyme called plasmin, which is involved in melanin synthesis. By regulating melanin production, it helps reduce brown spots associated with melasma. Melasma is often worsened by inflammation, and tranexamic acid has anti-inflammatory properties. By reducing inflammation, it improves the appearance of melasma-related pigmentation. It also works systemically to address pigmentation from within. This approach aims for a more balanced and uniform skin tone.
In addition, it is a medicine given as a blood thinner so proper consultation is needed prior to usage.
Glutathione Supplements
Glutathione, an antioxidant naturally produced in the body, is available in supplement form. Some individuals use glutathione supplements with the hope of achieving skin-lightening effects and reducing pigmentation. Glutathione acts as a potent antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. This can contribute to skin health and potentially help reduce pigmentation associated with melasma. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, glutathione may also influence melanin production. By modulating melanin synthesis, it may help achieve a more even skin complexion and reduce the appearance of brown spots in melasma. Glutathione has also been linked to collagen synthesis, which is important for maintaining skin elasticity and overall skin health. By supporting collagen production, glutathione may improve the quality of the skin and promote a more youthful appearance.
Pynocare – A Breakthrough Solution
Pynocare is an oral supplement that has gained popularity as a treatment for melasma. It contains a combination of natural ingredients, including procyanidin, vitamins C and E, and beta-carotene. Pynocare is believed to work by reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting melanin production, and improving skin health.
-
Procyanidin, Vitamins, and Antioxidants: Pynocare contains a combination of procyanidin, vitamins, and antioxidants. These ingredients work synergistically to address melanin production and support skin health.
-
Targeting Melanin from Within: Pynocare is an oral supplement that works from within the body. It influences factors like melanin synthesis, providing a comprehensive solution to pigmentation issues associated with melasma.
-
Balancing Skin Tone: Users of Pynocare often experience not only a reduction in the appearance of brown spots but also an improvement in overall skin tone and radiance. The supplement's multi-pronged approach contributes to a more balanced and luminous complexion.
Many users have reported positive reviews in reducing the appearance of brown spots and achieving a more even skin tone with regular use of Pynocare. Users have reported positive experiences with Pynocare, noting a gradual improvement in the appearance of brown spots and a more even skin tone. Many appreciate the fact that Pynocare addresses melasma from within, offering a holistic approach to skin health.
Precautions and Considerations
Sun Protection: Regardless of the treatment option chosen, it is crucial to protect the skin from sun exposure. Sunscreen with a high SPF should be applied daily, and protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses should be worn when outdoors.
Patch Test: Before using any topical treatment, it is advisable to perform a patch test on a small area of the skin to check for any adverse reactions or allergies.
Dermatologist Consultation: It is always recommended to consult with a dermatologist before starting any new treatment for melasma. They can assess your specific condition, recommend the most suitable treatment options, and guide proper usage and potential side effects.
Conclusion
Melasma can be challenging to manage, but there are a variety of topical and oral treatments available for these brown spots on the skin, providing hope for those looking to improve their skin's appearance. However, it is important to remember that everyone's skin is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. To ensure the best results, it is highly recommended to consult with a dermatologist who can provide personalized advice and guidance based on your specific needs. Additionally, it's important to prioritize sun protection, as excessive sun exposure can contribute to the formation of brown spots. By taking these steps, you can make significant progress in achieving clear and radiant skin.
Reference:
-
Melasma — Skin Conditions. We Care for Skin. https://www.wecareforskin.net/common-skin-conditions/melasma
-
Pynocare.ph. (2023, October 17). 5 Pynocare Reviews to Convince You to Try it for Your Melasma. https://pynocare.ph/5-pynocare-reviews-to-convince-you-to-try-it-for-your-melasma/
-
Banihashemi, M., Zabolinejad, N., Jaafari, M. R., Salehi, M., & Jabari, A. (2015, July 14). Comparison of therapeutic effects of liposomal Tranexamic Acid and conventional Hydroquinone on melasma. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 14(3), 174–177. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12152
-
Grimes PE, Ijaz S, Nashawati R, Kwak D. New oral and topical approaches for the treatment of melasma. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018 Nov 20;5(1):30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2018.09.004. PMID: 30809577; PMCID: PMC6374710.
-
Albzea W, AlRashidi R, Alkandari D, Sadan M, Alkandari A, Alkanderi JJ, AlHajri MT, Almutairi SN, Alenzi A, Alanazi S, Al-Qurashi S, Alhajaji R, Al Shami A. Azelaic Acid Versus Hydroquinone for Managing Patients With Melasma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cureus. 2023 Jul 12;15(7):e41796. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41796. PMID: 37457606; PMCID: PMC10339666.