know your skin
skin guide
Skin is the largest organ of the body, spanning over a whopping 20 square feet. Using a complex system of, glands, fat, blood vessels and connective tissue, it is indispensable to the proper functioning of the human body. The skin protects us from microbes, the elements, helps regulate body temperature and regulates sensory responses to touch, heat and cold.
Whilst preserving vital nutrients and chemicals in the body, it helps synthesize vitamin D and acts as a shield from harmful ultraviolet radiation emitted by the sun. Skin color, texture and folds are aspects inextricably linked to our overall well-being and to a great extent our identity and individuality too.
Anything that disrupts the proper skin function can potentially have major consequences for your physical as well as mental health. To that end, it is important to understand the layers of the skin to understand what it really is.
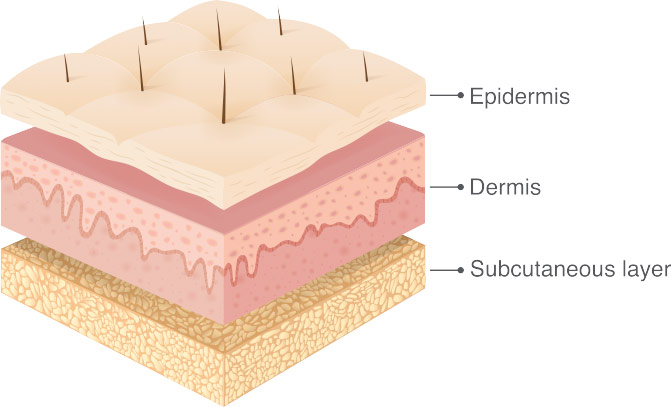
Human Skin Has 3 Layers
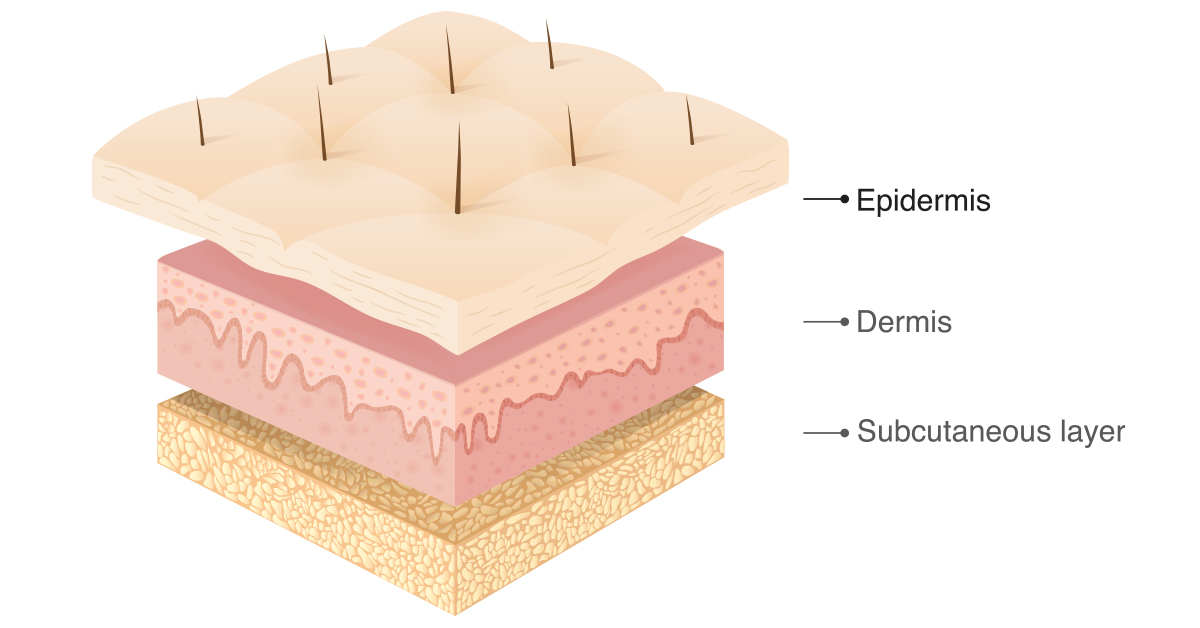
The Outer Layer
The outermost layer of your skin is called the epidermis. It acts as a barrier for your body, keeping out water and pathogens. It also has no blood vessels, being nourished by blood capillaries in the lowest layers,
Show more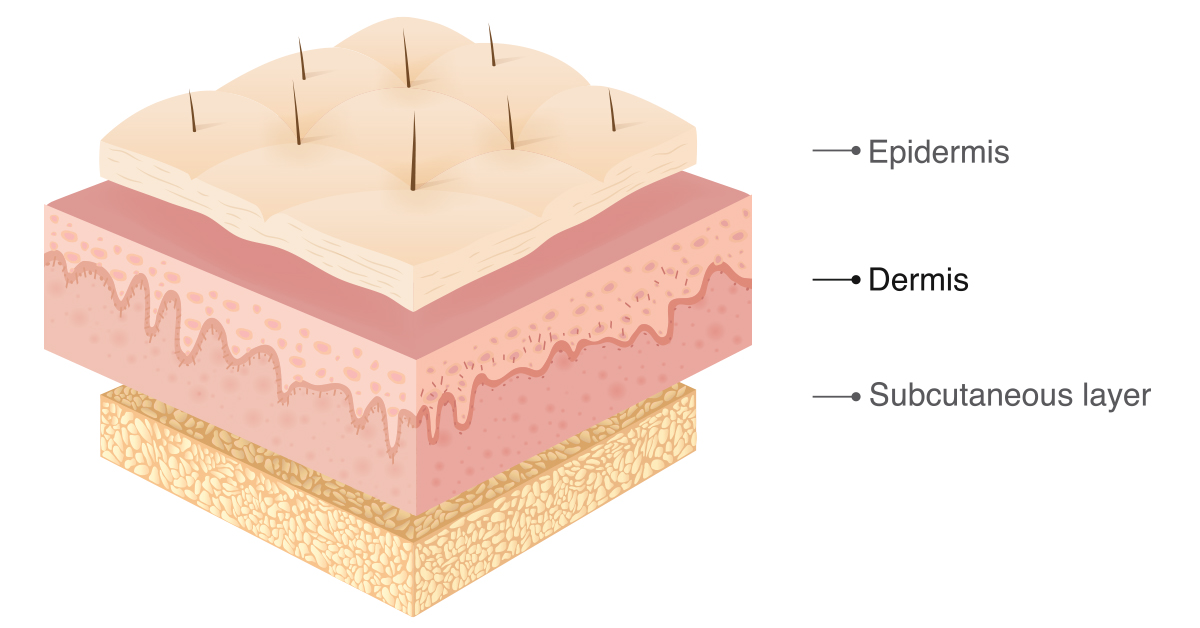
The middle Layer
Right below the epidermis is a layer called the dermis, mostly composed of connective tissue. This thick, fibrous layer is what makes your skin more elastic, as well as giving it tensile strength.
Show more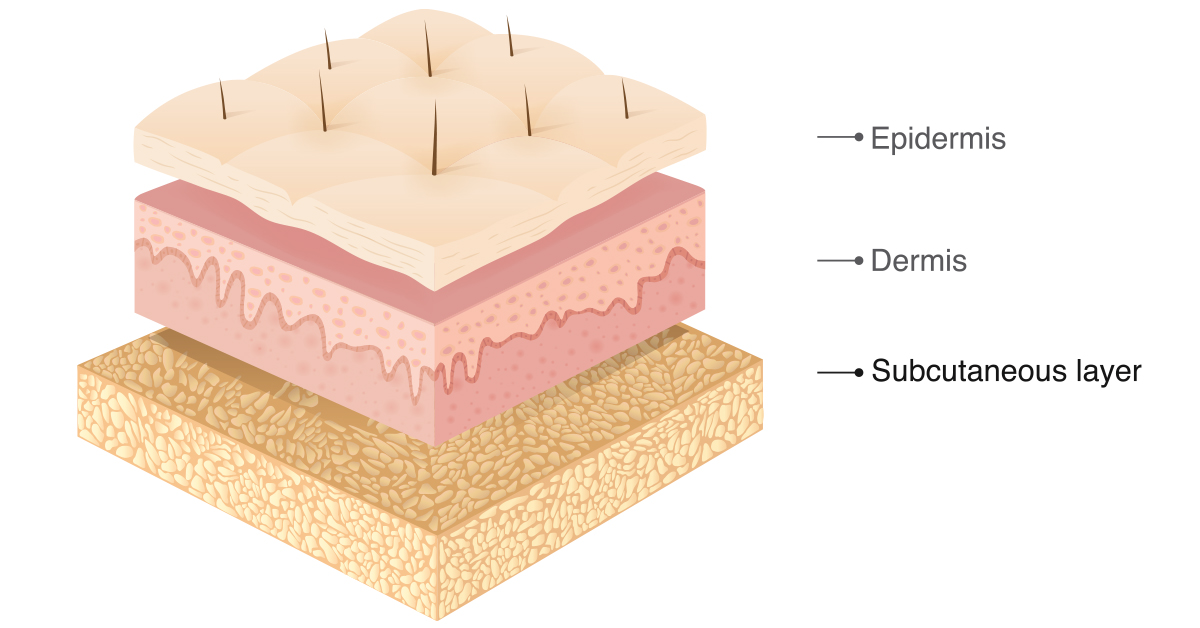
The Inner Layer
Also known as the ‘fat layer’, the hypodermis insulates the body from heat and cold, provides protective padding and stores energy reserves. It also serves to connect the upper layers of the skin to your muscles.
Show moreSkin Types
When it comes to classification, people are also categorized by the texture of their skin, such as oil, dry, or combination. This is important for dermatologists to recommend the best treatments for various skin conditions, including acne and dandruff. This classification usually refers to the skin on your face, though it sometimes matches the rest of your body as well. There are five main types.


Normal skin
This type of skin isn’t really called “normal” because it’s the norm, but rather because it has no glaring problems. Normal skin is neither too dry nor too oily, it’s not severely sensitive to anything, has barely visible pores, and can usually count on not having to deal with acne.
Oily skin
People with oily skin usually have enlarged pores and more overall sebum production than other types. This means the skin can either appear dull or shiny, depending on the amount of oil their glands produce, and is particularly susceptible to acne, especially blackheads and pimples. And that can be worsened by hormonal changes, stress, and too much heat or humidity. In this case, you’re going to want to use a gentle skin cleanser and not scrub, and wash your face no more than twice a day and after you sweat a lot. You’ll also need skincare and beauty products that are non-comedogenic, meaning they won’t clog your pores.
Dry skin
Dry skin has really tiny pores, almost invisible, and your skin can often look rough. It also feels less elastic, because of the decreased amount of sebum. Because of this, dry skin is especially susceptible to dry weather, especially in winters. It can become itchy or irritated and can develop cracks. Some factors like ageing, that make things worse, you can’t really avoid. You can and should however try to avoid cold weather and harsh sun, and long baths that can leach the oils out of your skin. Also try to regularly use a moisturizer after you bathe, to replenish your skin with what it needs.
Combination skin
Now, you might think it’s impossible to have skin that’s both dry and oily, but you’d be wrong. It’s possible for your skin to be dry or normal in some areas and oily in others. For instance, maybe your arms and legs have dry skin but your T-zone (nose, forehead, and chin) is oily. Combination skin usually also features large pores (at least on the face), and therefore is susceptible to acne. It’s actually a fairly common skin type, and needs different care methods based on the type of skin and part of the body.
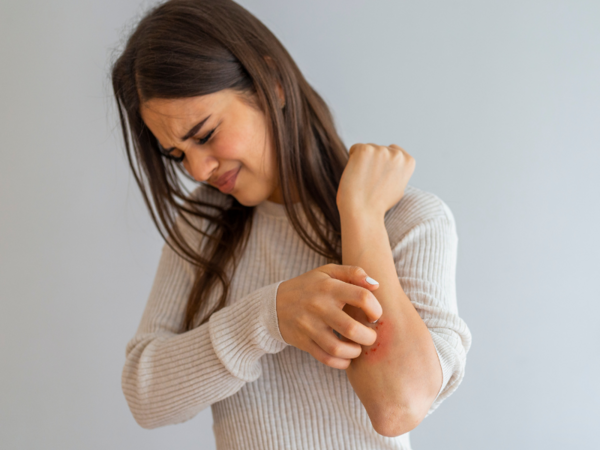
Sensitive skin
Sensitive skin is less of a type classification and more a measure of how easily it can become inflamed. This can show up as everything from simple redness to a full-blown rash or burning and itchiness. If your skin seems to often become inflamed, it’s advisable to visit a dermatologist and find out what triggers are causing the situation and avoid them.
Skin Color Types
It's not a secret that people worldwide have different skin colors, and most of us think it has something to do with a specific country's climate. While it's ultimately true, did you know that there are other reasons why our complexions tend to change over time and differ from one another? Let's delve deeper into this by discussing each skin color type objectively.
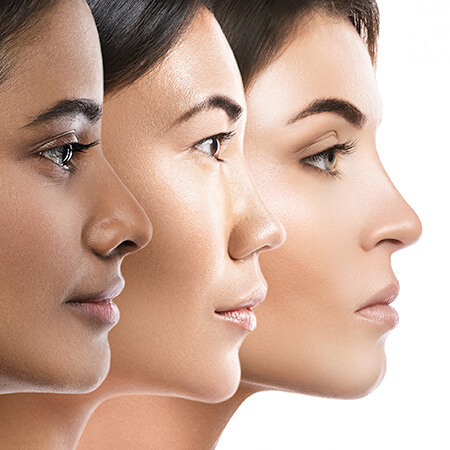


What your Skin Color Says About You
Human skin color ranges from lightest hues to the darkest tones, and that's a no-brainer. Throughout the years, experts have found a way to classify the response of specific skin types from the damaging UV rays by using the Fitzpatrick skin typing test. According to this scientific metric, the darkening of your skin color is often caused by the increased deposition of the pigment called Melanin.
You may not know it, but the amount of melanin pigment present on the surface highly determines the range of your skin color. Melanin is mainly produced by specialized skin cells called melanocytes, and this is the main indicator of skin tones for dark-skinned individuals.
Melanin pigment production comes in two main types. Eumelanin is the one that gives you the darker pigment, while Phemelanin gives you the lighter ones. In other words, the more Melanin that you have in your skin, the darker it will be.
Besides melanin pigmentation, your skin complexity can also be determined by several changing factors like hemoglobin blood count. This occurrence will contribute to the changes of your skin color upon the lack of oxygen saturation that makes its surface appear paler.
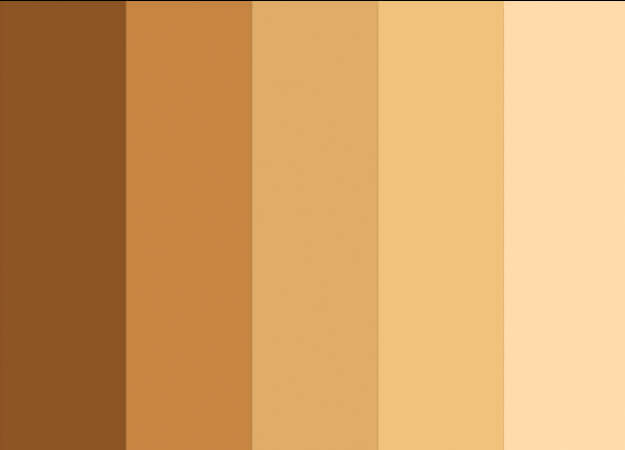
Skin color types
Admit it or not, knowing your skin tone helps you choose the appropriate shades of clothes, hair color, and make-up. To understand how your skin reacts to different conditions, here are the general color classifications you ought to know.
Pale
Pale is the lightest type of skin color. This type of complexion is normally seen in countries that experience snow or extremely cold weather conditions. Individuals with pale skin are most likely to get sunburns but do not tan because they lack Melanin. When doing intense exercises, they can easily turn reddish.
Fair
Fair skin is commonly found in Northeast Asian Countries and Europe. It is a type of skin color that burns easily but tans poorly. They tend to have this skin color because eumelanin is the dominant pigment on their skin surface.
Darker White
Unlike most paler skin types, people who have darker white complexions have the potential to get tan easier right after initial burns. It may look like dark patches, especially when mixed with a light skin tone.
Light Brown
A light brown skin tone means you have almost equal eumelanin and pheomelanin. Most Asian complexions fall in this category, and it's mainly because of genetics or geographic variation. When exposed to sunlight, the skin is prone to minimal sunburns, and the tanning behavior is highly uniform.
Brown
Most individuals with brown skin color have tan skin tones with golden undertones. This medium skin color tone is commonly found in Southern Europe and North Asian countries. Individuals with this type of skin color tend to get sunburns rarely but get darker tans easily.
Dark Brown or Black
Dark brown or black is the deepest among skin color ranges. This complexion is typically seen in tropical countries like India, Africa, and the Middle east. Individuals with dark skin tones rarely get sunburns and tan darkly. Considering the abundance of Melanin in their skin, people with this skin type have a relatively low risk of getting skin cancer.
Skin Essentials
Back when you were still a baby, you had soft and smooth skin. But as you grow older, breakouts and skin damages will ultimately become typical issues you have to deal with first-hand. And while it can be tough, the right skin essentials can easily help you prevent the frequent recurrence of these skin problems.
Benefits of Skin Care Essentials
No matter how old you are, taking good care of your skin includes many benefits. It’s an enticing journey, but starting skincare can be time-consuming and demanding. Despite that, we assure you that it will be easier to maintain once you establish your routine.
As many skin experts would say, skincare essentials can improve your skin texture and appearance. And because skin changes are one of the major indicators of aging, applying the right care package can maintain the youthfulness and radiance of your skin over time. As a result, it can help you boost your confidence and even encourage you to adopt a healthier lifestyle.
Basic Skin Essentials
As we all know, there is no general fine print of taking care of everyone’s skin. Many factors contribute to our skin condition, so not every popular facial product works the same for everybody. However, with proper maintenance, your skin can look way better than you expect it to be.
Here are few skincare essentials that we recommend to include in your skincare routine:

Facial Wash / Cleansers
Washing your face in the morning and before you go to bed is a vital part of your skincare routine. In fact, applying facial wash or cleanser on the surface of your skin is an excellent way of removing dead skin, oil, bacteria, and excess dirt that may clog your pores and turn into zits in the long run.
 "
"
Sunscreen
Sunscreen is an important product that you should never skip in your skincare routine. You may not know it, but excessive sun exposure has different effects on our skin that can result in uneven complexion or, worst, skin cancer. Sunscreen is the one that can protect your skin from accelerated aging and harmful UV rays from the sun.

Moisturizers
Moisturizing your skin can help prevent further breakouts. When you apply moisturizers, you are keeping your skin hydrated and free from dryness that could escalate to irritation. And while there are myths that moisturizers are only for people with dry skin, it’s actually good for maintaining a healthy balance between the moisture and oil production in our skin.

Supplements
Beauty supplements can give your skin the boost it needs to glow radiantly. Most skin essentials supplements come in capsules, powder, or liquid that are often readily available over the counter.






